Bladder Cancer
Bladder Cancer is a type of cancer that originates from the tissues that make up the structure of the bladder (urinary bladder). Bladder Cancer is the sixth most common cancer according to data from the United States. About 70,000 patients are diagnosed with bladder cancer every year in the United States, and about 15,000 people die due to bladder cancer. Although the incidence has increased over the years, there have been significant increases in the survival rates of the disease thanks to developing technology and treatment methods.
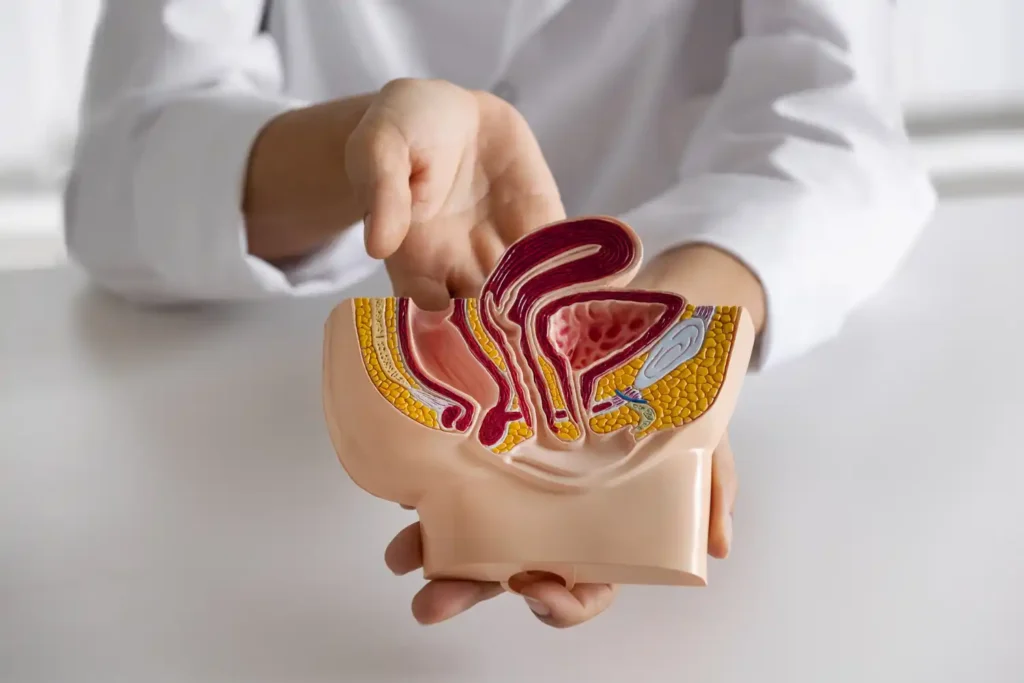
Having information about the structure and function of the bladder makes an important contribution to the understanding of bladder cancer. The bladder is an anatomically storage organ located inside the pelvis, where urine produced in the kidneys and transported through the urinary channels (ureters) is deposited at low pressure until voluntary urination occurs.
The bladder starts from the bladder, called the urethra, in both women and men, and continues with the urinary canal, which opens out and allows the urine to be drained. If it is to be described simply, it can be said that the bladder consists of 3 layers.
The bladder epithelium, which is in direct contact with urine in its innermost layer, the muscle layer (detrusor fibers) that surrounds the epithelium and contracts during urination, which allows the bladder to empty, and the outer membrane called serosa, which covers the muscle layer in the outermost layer, combine to form the bladder.
Risk Factors for Bladder Cancer
The most important risk factor for the development of bladder cancer is smoking. Carcinogenic substances that enter the blood through the lungs during smoking accumulate in the urine by filtering through the kidneys, except for the negative effects it has on various tissues and organs through the bloodstream. During the storage of urine in the bladder, it comes into contact with the epithelial tissue lining the inner part of the bladder and shows a carcinogenic effect on this tissue as well. As a result of research conducted, it has been shown that paints, solvents and various chemicals are also effective in the development of bladder cancer. The constant presence of carcinogenic substances in the urine in contact with the bladder epithelium causes more than 90% of bladder cancers to originate from this tissue.
Signs and Symptoms of Bladder Cancer
The most typical symptom for bladder cancer is the appearance of clotted or non-clotted bleeding (hematuria) in the urine, usually painlessly. Bleeding in the urine may sometimes not be visible to the eye and may also be detected in a urine test. Although every bleeding detected in the urine is not due to cancer, it should be carefully examined as it may be a sign of possible cancer. Except for bleeding, complaints of frequent urination and burning while urinating rarely can be symptoms of bladder cancer.
Diagnosis of Bladder Cancer
After a detailed history, including the use of tobacco and tobacco products and other carcinogenic exposures to be taken by the physician, a physical examination is performed. Ultrasound or tomography is performed to image the urinary tract. The most valuable diagnostic tool in terms of imaging bladder cancer is cystoscopy. Cystoscopy is a procedure in which the urinary tract is entered through an optical instrument and the bladder is viewed with a camera. In the detection of superficial tumors that cannot be detected with the naked eye, auxiliary tests such as urine cytology can also be used. In patients diagnosed with bladder cancer, the entire body is scanned using various imaging techniques, and it is also evaluated whether the cancer has spread to other tissues and organs.
Treatment of Bladder Cancer
The tumors detected in patients diagnosed with bladder cancer are scraped by means of the cystoscopic system. This procedure is called “Trans Urethral Resection (TUR)” because it is performed by entering through the urinary canal without making any incision in the body. After the tour, the tumor tissue obtained is sent to the pathology and examined, so that detailed information about the spread and type of cancer in the bladder can be obtained.
When planning treatment for bladder cancer, the placement of the tumor in the bladder, the pathological degree of the tumor, which layers the tumor holds in the bladder, whether it has spread to non-bladder organs, and the patient’s age and current health status are taken into account.
Bladder Cancer Surgery
The majority of bladder cancers retained only the bladder epithelium at the time of diagnosis and did not involve the muscle layer. Nov. This type of bladder cancer is called superficial bladder cancer, and LAP surgery is sufficient for treatment in most cases. In cases with superficial placement but high pathological degree, BCG (tuberculosis vaccine) or chemotherapy, which leads to destruction of tumor tissue by increasing the body’s immune response through a probe into the bladder, Oct, in addition to TOUR surgery, may be given. The patient is followed up intermittently with cystoscopy and imaging methods against the possibility of recurrence of the tumor.
The treatment of tumors that have retained the muscle layer by passing through the epithelial tissue located in the inner layer of the bladder is the removal of the entire bladder, called “Radical Cystectomy” surgery in the medical literature. Nov. When performing radical cystectomy surgery, the prostate gland in men and the uterus in women are almost always removed together. After the bladder is removed during Radical Cystectomy surgery, an open or closed bladder can be performed using the patient’s small intestine by different methods. Although Radical Cystectomy surgery can be performed with the open method classically, it can also be performed with the “Robotic Method” more minimally invasively in the light of developing technology.
In cases where the outer layer of the bladder (serosa) is retained by the tumor or the spread of cancer in other tissues and organs is detected, surgical methods are not preferred, systemic chemotherapy or radiotherapy are used as treatment options.